Peroneal Tendon Injuries
What Are the Peroneal Tendons? 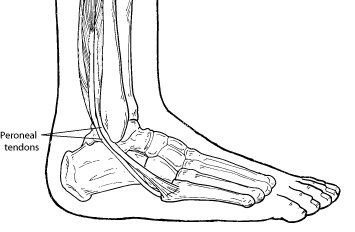
To understan peroneal tendon injuries, it's important to first understand what the peroneal tendons do. A tendon is a band of tissue that connects a muscle to a bone. The two peroneal tendons in the foot run side by side behind the outer ankle bone. One peroneal tendon attaches to the outer part of the midfoot, while the other tendon runs under the foot and attaches near the inside of the arch. The main function of the peroneal tendons is to stabilize the foot and ankle and protect them from sprains.
Causes & Symptoms of Peroneal Tendon Injuries
Peroneal tendon injuries may be acute (occurring suddenly) or chronic (developing over a period of time). They most commonly occur in individuals who participate in sports that involve repetitive ankle motion. In addition, people with higher arches are at risk for developing peroneal tendon injuries. Basic types of peroneal tendon injuries are tendonitis, tears and subluxation.
Tendonitis is an inflammation of one or both tendons. The inflammation is caused by activities involving repetitive use of the tendon, overuse of the tendon or trauma (such as an ankle sprain). Symptoms of tendonitis include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Warm to the touch
Acute tears are caused by repetitive activity or trauma. Immediate symptoms of acute tears include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Weakness or instability of the foot and ankle
As time goes on, these tears may lead to a change in the shape of the foot in which the arch may become higher.
Degenerative tears (tendonosis) are usually due to overuse and occur over long periods of time, often years. In degenerative tears, the tendon is like taffy that has been overstretched until it becomes thin and eventually frays. Having high arches also puts you at risk for developing a degenerative tear. The symptoms of degenerative tears may include:
- Sporadic pain (occurring from time to time) on the outside of the ankle
- Weakness or instability in the ankle
- An increase in the height of the arch
Subluxation means one or both tendons have slipped out of their normal position. In some cases, subluxation is due to a condition in which a person is born with a variation in the shape of the bone or muscle. In other cases, subluxation occurs following trauma, such as an ankle sprain. Damage or injury to the tissues that stabilize the tendons (retinaculum) can lead to chronic tendon subluxation. The symptoms of subluxation may include:
- A snapping feeling of the tendon around the ankle bone
- Sporadic pain behind the outside ankle bone
- Ankle instability or weakness
Early treatment of a subluxation is critical since a tendon that continues to sublux (move out of position) is more likely to tear or rupture. Therefore, if you feel the characteristic snapping, see a foot and ankle surgeon immediately.
Diagnosis of Peroneal Tendon Injuries
Because peroneal tendon injuries are sometimes misdiagnosed and may worsen without proper treatment, prompt evaluation by a foot and ankle surgeon is advised. To diagnose a peroneal tendon injury, the surgeon will examine the foot and look for pain, instability, swelling, warmth and weakness on the outer side of the ankle. In addition, an x-ray or other advanced imaging studies may be needed to fully evaluate the injury. The foot and ankle surgeon will also look for signs of an ankle sprain and other related injuries that sometimes accompany a peroneal tendon injury. Proper diagnosis is important because prolonged discomfort after a simple sprain may be a sign of additional problems.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of peroneal tendon injury. Options include:
- Immobilization. A cast or splint may be used to keep the foot and ankle from moving and allow the injury to heal.
- Medications. Oral or injected anti-inflammatory drugs may help relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy. Ice, heat or ultrasound therapy may be used to reduce swelling and pain. As symptoms improve, exercises can be added to strengthen the muscles and improve range of motion and balance.
- Bracing. The surgeon may provide a brace to use for a short while or during activities requiring repetitive ankle motion. Bracing may also be an option when a patient is not a candidate for surgery.
When Is Surgery Needed?
In some cases, surgery may be needed to repair the tendon or tendons and perhaps the supporting structures of the foot. The foot and ankle surgeon will determine the most appropriate procedure for the patient’s condition and lifestyle. After surgery, physical therapy is an important part of rehabilitation.
Why choose a foot and ankle surgeon?
Foot and ankle surgeons are the leading experts in foot and ankle care today. As doctors of podiatric medicine – also known as podiatrists, DPMs or occasionally “foot and ankle doctors” – they are the board-certified surgical specialists of the podiatric profession. Foot and ankle surgeons have more education and training specific to the foot and ankle than any other healthcare provider.
Foot and ankle surgeons treat all conditions affecting the foot and ankle, from the simple to the complex, in patients of all ages including peroneal tendon injuries, outer foot pain and peroneal tendon pain. Their intensive education and training qualify foot and ankle surgeons to perform a wide range of surgeries, including any surgery that may be indicated for peroneal tendon injuries.